Introduction
Self-driving vehicles are designs that combine the forces, such as AI models, which are trained to understand the world in the same way that a human does, i.e. recognising roads, cars, pedestrians, traffic signs, etc. in real time. Highly labelled data sets are the main determinant in creating models that can be accurate.
Here know how a poorly performing autonomous driving system turned into a safety, more reliable system through professional annotation services of Annotation Support.
1. The Challenge
An autonomous vehicle company faced:
- Pedestrian and cyclist’s false alarms are large.
- Minor and tiny partially covered subjects were at times misinterpreted as the subjects were not identified.
- Hazy spotting of low-light and wet situations
- Camera feed Delays Elevated delays in camera feeding data
What ails the fundamental dilemma? Improper and dissimilar data labelling of a previous outsourced company.
2. Project Goals
Annotation Support allocated the following techniques:
- Offering precision and re-annotation that is sustainable to old datasets
- Not only enlarging dataset to include edge conditions (e.g. driving at night, in snow, construction areas)
- Depth sense until you end up multiple sensor (camera, LiDAR) annotation
- It would conduct a stringent process of quality assurance (QA)
3. Annotation Techniques Used by Annotation Support
Bounding Boxes & Polygons – cars, trucks, buses, pedestrians and cyclists
Semantic Segmentation – Pixel Level label of roads, sidewalks, curbs, lanes lines
LiDAR 3D Point Cloud Annotation depth / distance – LiDAR labelling
Keypoint Annotation – Wheel locations, headlight locations, locations of joints of pedestrians to make predictions of moving direction
Occlusion & Truncation Labels -Marking the truncated or occluded objects of the detection training
4. Quality Control Measures
- Clear guidelines on annotation so far as they are in line with the perceived requirements of the AV company model
- Multi-annotator-review system where inconsistency is, allowing inconsistency to be identified
- Efficiency in use of AI aided pre-labeling and post human verification
- A performance feedback loop: Statistics distribution within the model was optimised by the use of annotation performance statistics to optimise distribution therein
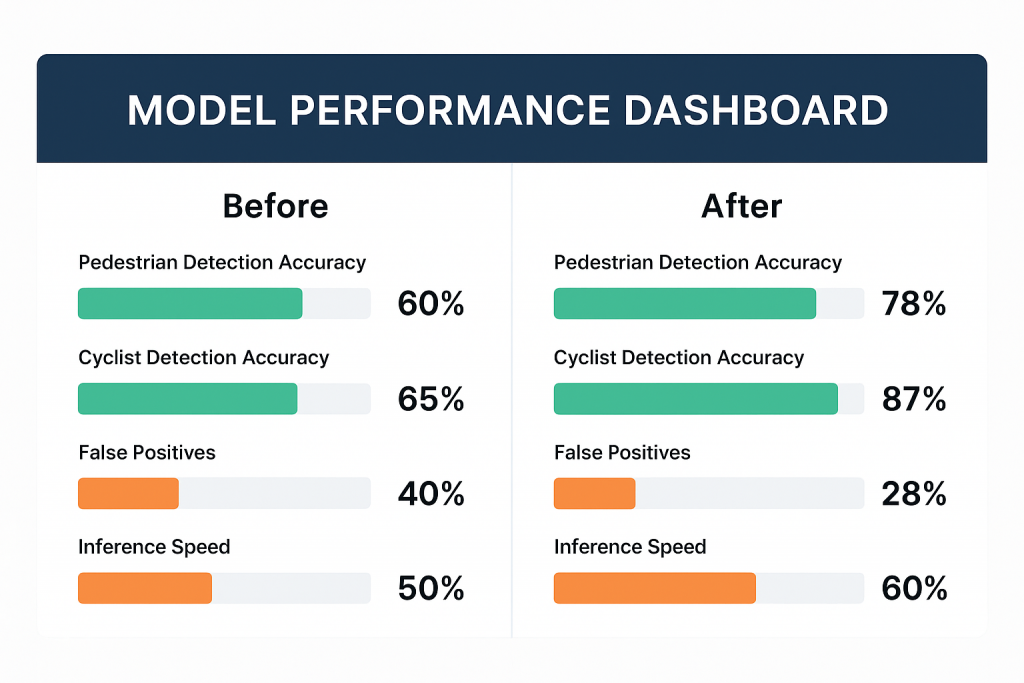
5. Results
One quarter-year later, having been re-annotated, and the data set scaled up:
- The pedestrian detection was increased by 18 percent.
- There was a 22 per cent improvement in the accuracy of bicycle detection
- Improvement in rainy conditions and night time False positives were decreased by 30 percent
- The inference speed of models was faster because data were clean and well structured.
- More safe operation in tricky Intersections and construction sites
6. Learning Key Points
- Edge cases are essential – Real life driving is done in uncommon but dangerous situations.
- Steady wins the race Over thousands of frames consistency in labeling is more important than making annotations incredibly fast.
- The key challenge here is multi-sensor synergy – combined camera and LiDAR allowed depth perception and tracking to be improved.
- This is because regular updates in the dataset are mandatory since the traffic patterns and environments keep changing.
Conclusion
Annotation Support does not only deliver labeled data–clean, consistent, context-aware annotations were directly contributed to better results in the AI judgment. In autonomous driving, the quality of the data obtained about perception may mean the difference between a near miss and accidents. With high-quality annotations, the self-driving car model became safer, faster, and more reliable—bringing it one step closer to real-world deployment.