Blog
Top 10 Data Annotation Companies 2026
Artificial Intelligence in 2026 is no longer experimental. It is operational, embedded, and revenue-driving. But behind every successful AI system...
Read More
The Role of Image Recognition in Creating Smart Cities
Smart cities are based on new technologies to enhance the city life. Image recognition (computer vision) is one of these...
Read More
The Secret Revealed: Quality Control Techniques Used by Annotation Support in Data Annotation Projects
Ensuring high-quality annotated data is the backbone of any successful AI or machine learning system. But maintaining accuracy at scale...
Read More
AI in Agriculture: How Annotated Data Is Feeding Smart Farming?
Agricultural industry is going through the digital revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is assisting farmers to make quicker, smarter and more...
Read More
How Annotation Support offers Video Annotation Services for Retailers In-Store Analytics?
With the current retailing landscape, which is rich with data, the study of customer behaviour within a store is just...
Read More
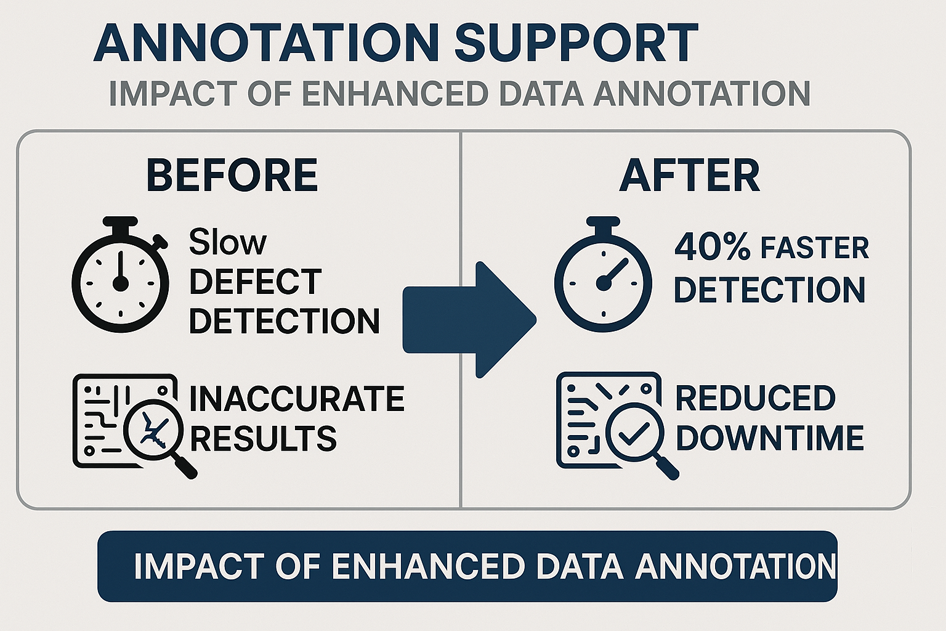
Detecting Defects Faster: Annotation Support’s Work with a Global Electronics Manufacturer
In the highly competitive electronics industry, even the smallest defect can have a ripple effect—delays in production, increased costs, and...
Read More
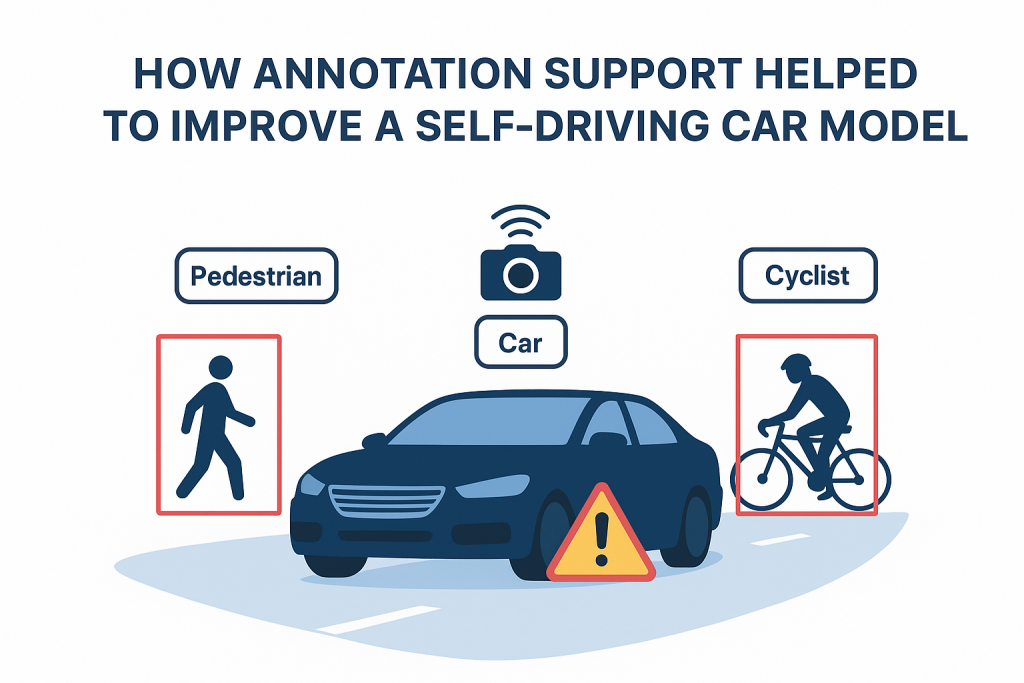
How Annotation Support Helped to Improve a Self-Driving Car Model?
Introduction Self-driving vehicles are designs that combine the forces, such as AI models, which are trained to understand the world...
Read More
Top Annotation Techniques Used in Autonomous Vehicle Datasets
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on high-quality annotated data to interpret the world around them. From understanding traffic signs to detecting...
Read More
Exploring the Top 5 Challenges in Annotating 3D Point Cloud Data from LIDAR: Solutions and Best Practices
The LIDAR ( Light Detection and Ranging ) technology has become one of the foundations of a number of advanced...
Read More
Load More